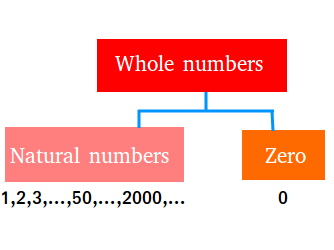
Whole Numbers
The set of whole numbers include the natural numbers and 0. Suppose we call this set W, then W = { 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,......}. Natural number, also called counting numbers, are 1, 2, 3, 4...
The number line below only shows whole numbers from 0 to 10. However, not all numbers are shown!
50 is also a whole number. Similarly, 2000 is also a whole number as the following figure shows.
See Below Two Graphs Showing What Whole Numbers Are

Physical Representations of Whole Numbers
Cubes can be used to represent numbers|
1 cube: physical representation of 1 |
|
|
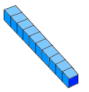
1 long : physical representation of 10 Made of 10 cubes. |
 |
|
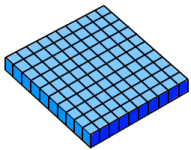
1 flat : physical representation of 100 Made of 100 cubes. |
 |
|
1 block: physical representation of 1000 Made of 1000 cubes. |
 |
Let's say you have 4 blocks, 8 flats, 5 longs, and 8 cubes.
What whole number is this?
1 block represents 1000, so 4 blocks represent 4000
1 flat represents 100, so 8 flats represent 800
1 long represents 10, so 5 longs represent 50
1 cube represents 1, so 8 cubes represent 8
4000 + 800 + 50 + 8 = 4858
Why do we Need Whole Numbers?
Everybody counts, adds or subtracts on a daily basis. From the time we started counting toys on the floor when we were 2 or 3 years old to when we count the cost of our groceries we need numbers.A child counting cubes for instance may want to know how many cubes the following set has.
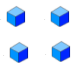 Representation of 4 Representation of 4 |
The numeral that we use to represent the set above is 4
When using numbers to count how many elements a set has, it is referred to as cardinal numbers. For instance, 4 or four is a cardinal number.
What Types of Numbers are out there besides Whole Numbers?
These are integers, rational numbers, irrational numbers real numbers, and complex numbers.
We will not cover these here, we will only focus on whole numbers in this unit, but be aware that they exist.
If you are really curious, visit the following website: Wikipedia
Knowing about operations with numbers can be an invaluable tool as we go about our daily routine.
My goal is to help you discover the similarities among addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and many others.
Before knowing how to add, subtract, multiply and so forth, it is important to understand place value. Next, take the quiz and then study the lesson about place value.