Standardizing a normal distribution
Standardizing a normal distribution is to convert a normal distribution to the standard normal distribution. In real-world applications, a continuous random variable may have a normal distribution with a value of the mean that is different from 0 and a value of the standard deviation that is different from 1.
In this case, we need to standardize the normal distribution so we can use the standard normal distribution table to find areas or probabilities under the normal curve.
The units of a normal distribution are denoted by x and the units of a standard normal distribution are denoted by z.
The formula to use when standardizing a normal distribution is the standardized scores
μ and σ are the mean and standard deviation of the normal distribution of x.
Example #1
Let x be a continuous random variable that is normally distributed with a mean of 30 and a standard deviation of 4. Find the area between x = 30 and x = 39
The first step is to standardize the given normal distribution by converting x = 30 and x = 39 to respective z values using the formula above.
For x = 30,
For x = 39,
Area under the normal curve between x = 30 and x = 39 is the same as the area under the curve between z = 0 and z = 2.25
P(30 < x < 39) = P(0 < z < 2.25)
Using the technique in the lesson about area under the standard normal curve we see that P(0 < z < 2.25) = 0.4878
Example #2
Let x be a continuous random variable that is normally distributed with a mean of 50 and a standard deviation of 6. Find the area between x = 41 and x = 59
The first step is to standardize the given normal distribution by converting x = 41 and x = 59 to respective z values using the formula
For x = 41,
For x = 59,
Area under the normal curve between x = 41 and x = 59 is the same as the area under the curve between z = -1.5 and z = 1.5
P(41 < x < 59) = P(-1.5 < z < 1.5)
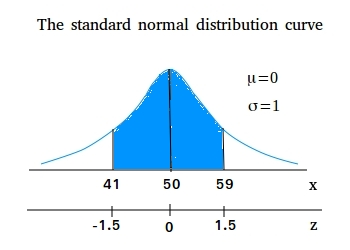
P(-1.5 < z < 1.5) = P(-1.5 < z < 0 ) + P(0 < z < 1.5)
Since the normal distribution is symmetric, P(-1.5 < z < 0 ) = P(0 < z < 1.5)
Using the standard normal distribution table, P(0 < z < 1.5) = 0.4332
P(-1.5 < z < 1.5) =0.4332 + 0.4332 = 0.8664