What is elasticity?
What is elasticity? Most of us have played before with a piece of
elastic or rubber band. Unlike many other things you encounter daily, a
rubber band can be stretched to a certain extent. When things can be
stretched, people usually say that that thing is elastic.
However, in physics the two phenomena below must be present before we can say that an object is elastic.
1. A change in shape when a force is applied
2. A return to its original shape when the force is removed
Do these apply to the elastic band? Yes.
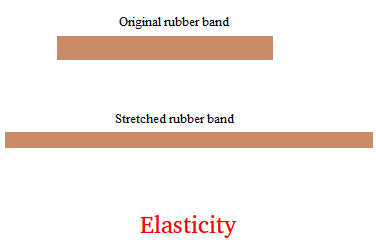
1. When a force is applied to an elastic band in order to pull the elastic, the elastic band does not only allow itself to be stretched, it is also deformed or shrunk.
2. When the force is removed, the elastic return to its original shape .
Other examples of elastic objects:
A spring: Hang a weight on a spring.
1. The spring will stretch. Hand a bigger weight, the spring will stretch even more.
2. When the weight is removed, the spring will return to its original shape or length.
A bow: Shoot an arrow
1. The bow is bent before the arrow is released
2. The bow returns to its original shape after the arrow is released.
A trampoline: Bounce on an trampoline
1. Every time your feet hit the bounce mat, it deforms it.
2. Every time your feet are in the air, the bounce mat returns to its original shape.
Inelastic objects:
When phenomenon 2 fails to happen or the object does not return to its original shape, we say that the object is inelastic. Examples of inelastic objects are clay, dough, and putty.
An elastic material can be stretched or compressed so much that it will not return to its original shape but remain distorted. We say that the material has reached its elastic limit.
If you hang a weight on a spring that is a lot heavier than what the spring can handle, the spring will remain distorted.
What is elasticity? Hooke's law
Say you hang a weight on a spring
Physicist Robert Hooke said that the amount of stretch (x) the spring experience is proportional to the amount of force (F) applied.
In other words, if the force is doubled, the stretch will also double.
If the force is quadrupled, the stretch will also quadruple.
Mathematically, this can be expressed as F = kx
Say for instance a force of 6 N is applied and the spring stretches 2 cm. When the force is 12 N, the spring stretches 4 cm.
Observation:
6 = 3 × 212 = 3 × 4
F = 3 × x
k = 3 and is called the spring constant