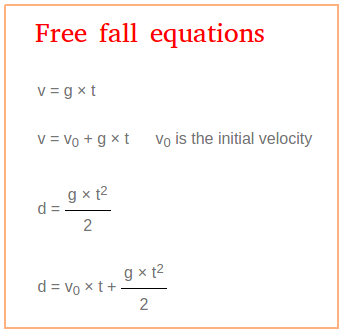
Free Fall Equations
The free fall equations are shown below for free falling objects. In order for you to understand how we found these equations, it is important to understand speed, acceleration, free fall, and acceleration due to gravity.
You may need to carefully review the lessons about speed and acceleration.
What is free fall? Whenever an object is dropped in the air from a certain height, this object is falling. The object is not experiencing free fall just yet. Why do we say so?
If you drop a feather and a piece of rock from the second floor of a house or building, the rock will accelerate faster and get to the ground faster.
This happens because of air resistance. However, if you put the feather and the rock in a tube and remove the air with a vacuum pump, the feather and the rock will have the same acceleration.
Conclusion:
Objects experience free fall when there is no air resistance or when air resistance is negligible.
Now, it makes sense why we say free fall equations. It is because they are found when objects are affected only by gravity but air resistance is negligible.
Now, let us try to find the acceleration due to gravity only.
If you could drop a rock from the 10th floor of a building and equip the rock with a speedometer that can record the instantaneous speed during each second, you will end up with the following data:
|
Elapsed time in second(s) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 t |
Instantaneous speed in m/s 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 10t |
Remember that the formula to find the acceleration is
The acceleration is 10 m / s2
10 m / s2 is read 10 meters per second squared.
Where did the exponent of 2 come from? A little bit of math may help.
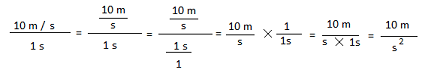
If you did not understand the math above, visit the lesson about dividing fractions.
Since the acceleration is due to gravity, we use g and write g = 10 m / s2. Keep in mind though that g is not the same everywhere in this world.More accurately, g = 9.8 m / s2
From the data we see that 20 = 10 m/s × 2 or 50 = 10 m/s × 5
In general, v = g × t
If the object is thrown with an initial velocity, the equation is v = v0 + g × t and v0 is the initial velocity.
When an object is thrown upward or straight up with an initial velocity, the object is still subject to gravity. Moreover, the speed will decrease until it reaches 0.
Therefore, the speed will decrease by 10 m/s each second.
When the highest point is reached and the speed is 0, it will start going down and increase by 10 m/s each second.
We have found two free fall equations so far dealing with how fast. What about how far the object moves?
Free Fall Equations: How far ?
total distance = average speed × total time
How do we find the average speed? Using our data, what is the average speed from 0 to 10 m /s ?
For any object moving in a straight path with constant acceleration, we find the average speed the same way we find the average of two numbers. So, the average speed between 0 and 10 m /s is
Average speed = 5 m / s
To get the speed at any instant, we can use v = g × t. Thus, the same formula can be used to get the final speed.
Multiply the average speed by the total time or t